Essential Website Maintenance Checklist for 2025: Keep Your Site Running Smoothly

Proactive Website Maintenance: How to Prevent Downtime and Boost Reliability
Keeping a website healthy in 2025 is a continuous process—not a one-time task. Search engines reward fast, secure, and stable sites, while users expect flawless experiences on any device and connection speed. This maintenance playbook gives you a practical, repeatable plan to protect your site, improve performance, and reduce downtime. Whether your stack is WordPress, Shopify, Webflow, or a custom framework, the principles below will help you run a resilient website that ranks higher, converts better, and costs less to operate.
Why maintenance matters now
Modern websites are dynamic. Content changes, plugins evolve, APIs shift, and traffic patterns spike without warning. Neglecting maintenance leads to a pile-up of small issues—outdated dependencies, slow pages, broken CTAs—that eventually become outages, SEO drops, and lost revenue. A disciplined maintenance process prevents regressions, keeps your team accountable, and turns your site into a durable asset.
The maintenance framework: Secure → Perform → Observe
Think of maintenance as a cycle:
- Secure: Patch vulnerabilities, enforce least-privilege access, and harden your stack.
- Perform: Optimize delivery (images, CSS/JS, caching, CDN) and trim page weight.
- Observe: Monitor uptime, errors, and Core Web Vitals; use data to guide the next sprint.
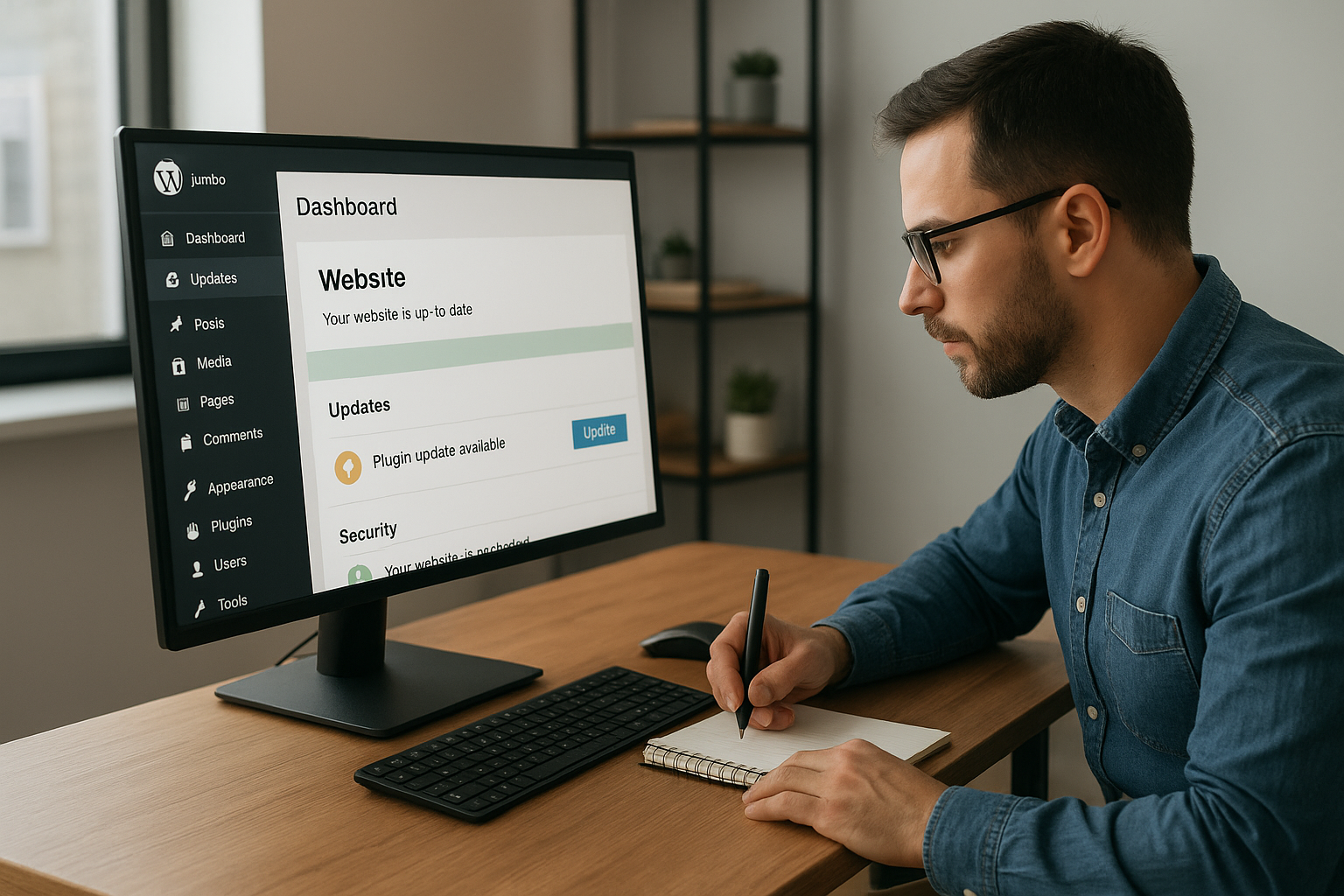
Monthly security hardening checklist
- Patch management: Update CMS core, themes, plugins, dependencies (npm/composer/pip), and server packages.
- User access review: Remove stale accounts, rotate admin/API credentials, and enforce MFA for admin panels.
- WAF & firewall rules: Enable a Web Application Firewall, rate-limit suspicious IP ranges, and block common attack vectors.
- HTTPS by default: Enforce HSTS, redirect HTTP→HTTPS, and renew/auto-renew TLS certificates.
- Database hygiene: Change default table prefixes (where applicable), restrict remote DB access, and audit DB users/roles.
- Secure uploads: Limit executable file types, scan media for malware, and use object storage when possible.
- Backup integrity test: Perform a test restore on staging to verify your backups actually work.
Performance optimization tasks
- Image pipeline: Convert large assets to WebP/AVIF, resize to responsive breakpoints, and lazy-load below-the-fold images.
- CSS/JS delivery: Inline critical CSS for above-the-fold content; defer non-critical scripts; remove dead code.
- Caching strategy: Set sensible cache-control headers, use CDN edge caching, and implement server/page caching for dynamic CMS pages.
- Font strategy: Use system fonts or host fonts locally; preconnect to font origins and subset character sets.
- Third-party governance: Audit tags and widgets (analytics, chat, ads). Remove or lazy-load non-essential vendors.
Core Web Vitals (CWV) guardrails
Google’s CWV remain critical signals:
- LCP (Largest Contentful Paint): Optimize hero images, reduce server TTFB, and prioritize critical resources.
- INP (Interaction to Next Paint): Reduce main-thread blocking work; split heavy scripts; prefer progressively enhanced features.
- CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift): Reserve space for media/ads and avoid injecting content above existing content without space.
Weekly quick-check routine (15–30 minutes)
- Uptime & SSL: Confirm 99.9%+ uptime, valid certificates, and no recurring incidents.
- Forms & CTAs: Submit key forms (contact, quote, checkout) and verify email/CRM integrations.
- Error logs: Scan application/server logs for PHP/JS errors, 5xx spikes, or API timeouts.
- Speed spot-check: Run Lighthouse or PageSpeed on top landing pages; compare to baselines.
- Content sanity: Check for broken images, typos on latest posts, and date-sensitive content.
Quarterly deep-dive audit
- Technical SEO: Crawl the site for broken links/redirect loops, validate sitemaps, and review robots directives.
- Information architecture: Simplify navigation, prune thin/duplicate content, and strengthen internal linking.
- Accessibility: Evaluate color contrast, focus states, alt text coverage, and ARIA on interactive components.
- Scalability test: Load-test critical paths (home, PDP, checkout) and verify autoscaling/CDN behavior under stress.
- Disaster recovery drill: Restore the latest backup to staging, run functional tests, and document RTO/RPO results.
Backup strategy that actually saves you
A backup you can’t restore isn’t a backup—it’s a false sense of security. Use a 3-2-1 approach: three copies of your data, on two different media, with one copy off-site. Automate daily incrementals and weekly full backups. Encrypt archives and store at least one copy in a separate cloud provider. Schedule quarterly restore drills and keep runbooks updated with screenshots and timestamps.
Hardening your infrastructure
- Principle of least privilege: Tighten permissions for SFTP/SSH, DB, and CMS roles; segregate staging/production keys.
- Isolation: Use containers or separate hosting accounts to prevent cross-site contamination.
- Headers & policies: Add security headers (CSP, X-Frame-Options, X-Content-Type-Options, Referrer-Policy) to reduce exploit surface.
- Rate limiting & bot control: Throttle login endpoints and protect search/API endpoints from scraping or brute-force attacks.
Content & compliance upkeep
- Policy pages: Review privacy policy, terms, returns/refunds (for eCommerce), and cookie consent behavior.
- Data lifecycle: Purge PII you no longer need; document retention schedules; mask test data in staging.
- Analytics governance: Ensure consent mode (where applicable) and maintain a catalog of tracking scripts.
Observability: turn noise into decisions
Monitoring should be actionable, not overwhelming. Set alerts for uptime drops, 5xx error rates, and CWV regressions. Track a concise KPI set: conversion rate, average page load (mobile), server TTFB, error percentage, and form submission success. Build dashboards that compare week-over-week and month-over-month trends so you can spot regressions early.
Staging-first deployment workflow
- Commit changes to a version-controlled repo; run automated tests (lint, unit, visual diffs if available).
- Deploy to staging; validate forms, payments, search, and dynamic components.
- Run Lighthouse and accessibility checks on staging; fix blockers.
- Schedule production release during low-traffic windows; monitor logs and roll back fast if needed.
Red flags that demand immediate action
- Sustained 5xx errors or CPU spikes on the origin server.
- Unexpected traffic from a single ASN/IP block (possible attack or crawler gone rogue).
- Sudden drop in organic traffic or CWV scores after a deployment.
- Increased chargebacks or abandoned checkouts (may indicate performance or payment gateway issues).
Documentation & ownership
Create a living maintenance document that lists owners, schedules, SLAs, and playbooks:
Who is responsible for patches and backups; when tasks run; where runbooks live; and how to roll back. Good documentation cuts incident time by half and makes handovers painless.
Quick-start 30-day plan
- Day 1–3: Baseline audit (security, performance, SEO, accessibility). Set KPIs and create dashboards.
- Day 4–10: Patch, enable MFA, harden headers, implement WAF rules, and prune unused plugins.
- Day 11–18: Image pipeline to WebP/AVIF, defer JS, configure CDN caching, and fix top 10 slow pages.
- Day 19–24: Backup automation (3-2-1), offsite storage, and first restore drill on staging.
- Day 25–30: Document processes, assign owners, and schedule weekly/monthly routines.
Conclusion
Great websites aren’t just beautifully designed—they’re well maintained. With a repeating Secure → Perform → Observe cycle, disciplined patching, smart caching, robust backups, and data-driven monitoring, your site will be faster, safer, and more reliable than competitors who still treat maintenance as an afterthought. Start with small wins this week—patch, compress, and test a restore—and build momentum toward a maintenance culture that compounds results every month.